Overview of available RDO repos
There are a number of different repos that the RDO project works out of. This is an overview of each of them.
NOTE: Overview and comparison of RDO's deliverables can be found in this article.
RDO CloudSIG repositories
Provide a set of stable OpenStack packages through CentOS CloudSIG repos based on CBS, CentOS Community Build System:
- The RDO CloudSIG repos are only published after GA of a upstream release (only stable branches are used, not master).
- New packages are created only when a new point release is published (release tag created) on upstream stable repositories.
- In addition to the vanilla upstream code, some patches may be applied during packaging:
- Fixes for security issues or critical bugs not backported upstream. Note that an upstream-first policy is applied so these patches will be applied only after merged in upstream master.
- Patches required for the packaging process.
For each OpenStack release RDO provides two repos:
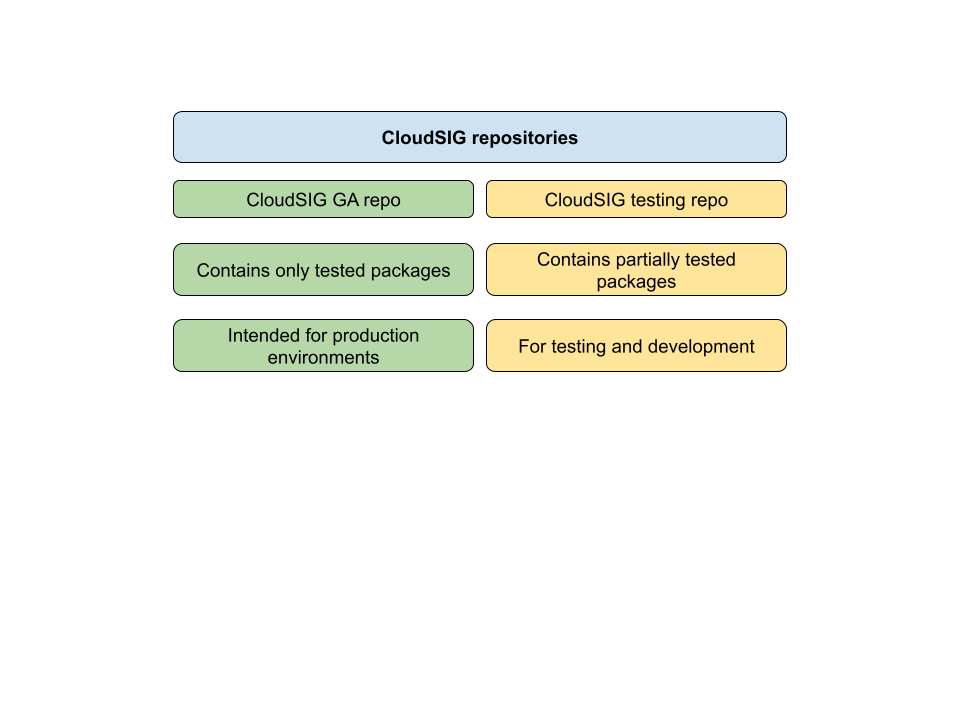
CloudSIG GA repo
The GA repository is the one you should be using for your production environment. It contains tested, digitally signed packages.
To enable this repository on a CentOS system, run the following command:
For CentOS Stream 9:
$ sudo dnf install centos-release-openstack-<release>
Where <release> is the name of the OpenStack release you want to install. The RDO community supports the same OpenStack releases supported by upstream.
On a non-CentOS system (e.g. RHEL), you can run the following command to setup the RDO GA repositories:
For the latest OpenStack release in RHEL 9:
$ sudo dnf install http://trunk.rdoproject.org/rdo_release/rdo-release.el9s.rpm
For previous OpenStack releases in RHEL 9:
$ sudo dnf install http://trunk.rdoproject.org/rdo_release/openstack-<release name>/rdo-release-<release name>.el9s.rpm
This will configure the repositories for the most recent version of RDO. RPMs for previous releases are accessible from this location.
CloudSIG Testing repo
The testing repository contains packages that have not gone through our complete test suite. These packages can be useful to test newer versions of the code, or when you need to quickly deliver a hotfix to your production environment. Please keep in mind that packages from the testing repository are not digitally signed.
If you enabled the RDO repositories using the centos-release-openstack-* RPM, run the following command to enable the testing repository:
$ sudo yum-config-manager --enable centos-openstack-<release>-test
If you used the rdo-release RPM, run the following command:
$ sudo yum-config-manager --enable openstack-<release>-testing
Comparison of CloudSIG GA repo and testing repo
RDO Trunk repositories
RDO Trunk repositories are built using the most recent commit from each of the OpenStack projects. They are used in different ways:
- By several OpenStack CI jobs, to test packages built from the current under-development branch.
- Internally by the RDO community, to ensure that our packaging pipeline is always up to date.
- They can also be used to deliver hotfixes for stable releases, as soon as the relevant patch has been merged in the upstream repos.
The RDO Trunk packages are not digitally signed, and have gone through some minimal CI. You can enable the CI-passed RDO Trunk repo using the following command:
$ sudo yum-config-manager --enable rdo-trunk-newton-tested
If you need a package using the latest commit, even before it passes CI (be aware this is bleeding edge!), go to the RDO Trunk web.